AWS-2
AWS Migration: Migrating An On-Premise Application To Cloud
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Irrespective of the business, organizations always experience competition. Hence staying updated with the market needs, becomes a must, and ‘time’ becomes an integral constituent. What if there was a way business could focus on their business goals and outsource their maintenance and monitoring tasks somewhere else. Would that help save time & meet the market needs with more efficiency? Migrating to cloud lets you do exactly the same. This AWS Migration article would walk you through all the necessary pointers that you need to consider before you plan to migrate to Cloud.
For starters, let me define Migration for you:
Now that the definition is out of the way, let’s take a look at the pointers the article focuses on:
Before we jump in, do check out the important AWS topics that are required to master AWS. Let’s begin by understanding the need for Migration.
Need for Migration
Business is no easy task when it comes to handling situations like security, scaling up or down, etc. Let’s look at a few scenarios where AWS Migration could be a better resort.
- Your project has started receiving a high volume of traffic overnight
- Your clients want fast application implementation and deployment
- It’s becoming expensive to manage the growing database needs
- You are cautious about the mishap of data center going down
If you Migrate to Cloud then the problems mentioned above will get handled automatically. Let’s move further and understand what is Migration.
What is Migration?
Migrating your project means moving your data from the on-premise data center to cloud. FYI we are not referring to clouds in the sky. In this case, cloud is the virtualization used over a data center to make the functionalities more flexible. Many companies like GoDaddy, Expedia etc., have recently moved their business to cloud.
Having defined Migration, let me tell you where, how, and who is going to help you migrate your data. The implementation is provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). So, let’s find out what AWS is?
You can learn more here: What is Cloud computing?
What is AWS?
 Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com which provides on-demand cloud services. AWS made a debut in 2006 with a few services. Then, in 2012 launched the AWS Marketplace that accommodated a vast range of services provided by AWS.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com which provides on-demand cloud services. AWS made a debut in 2006 with a few services. Then, in 2012 launched the AWS Marketplace that accommodated a vast range of services provided by AWS.
Again, Migration is a big task and AWS facilitates Migration in phases. So, let me walk you through the different phases of Data Migration.
Phases of AWS Migration
Data Migration seems an easy process because in layman’s term, it means moving your data from one location to the other. However, it is more complex as the process involves different phases. Let me now talk about the various phases of Migration:
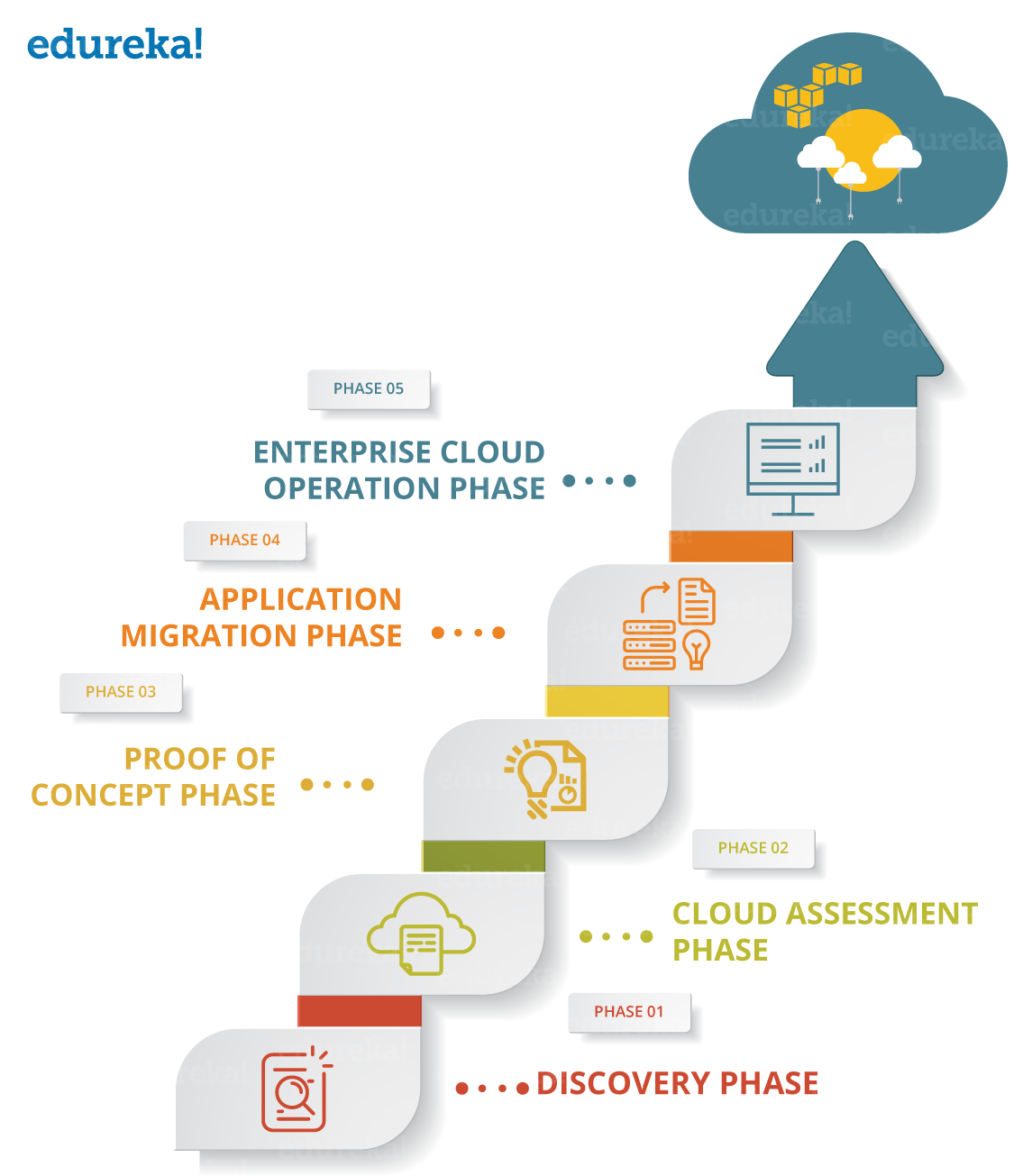
Phase 1: Discovery – Apps which can be moved to Cloud?
There are times you need not require to move your entire business to the cloud.This is where segregation is important. You need to identify the applications which can be Migrated and which cannot. This is what the first phase is all about. Now, let’s go to Phase 2 i.e. choosing the method for AWS Migration.
 Phase 2: Assessment – Choosing Your Migration Method
Phase 2: Assessment – Choosing Your Migration Method
Depending on the data, AWS provides different ways to Migrate your application e.g. AWS Snowball, AWS Snowmobile, AWS Direct Connect, etc. Once you have chosen an appropriate way to move your data, also look for the resources you’ll need for it. Let’s now explore the different ways of storing data on AWS Cloud in Phase 3.
Phase 3: Proof of Concept (POC) for AWS Storage
Once you know how and what you are migrating, next, you have to figure out how and where you will store it. The entire motive of moving to AWS is to minimize expenses. In this phase, you’ll test your workload and understand about AWS Storage Service, their benefits, limitations, and the necessary security controls.
 Phase 4: Application Migration to AWS
Phase 4: Application Migration to AWS
Now that you have all the pre-requisites like the blueprint, Migration tools, list of assignments, backups and its synchronization with your on-premises data repositories. You can finally migrate your project to AWS Cloud. Once you have Migrated your project to cloud, reliability, and durability are the added benefits you get. Let’s see the changes AWS brings to your architecture in Phase 5.
Phase 5: Enterprise Cloud Operations
At this point, you’ve already migrated to AWS, and AWS will bring updates that you’ll need to incorporate in your existing architecture. Hence, you must ensure that you have a 24×7 support team keeping track of system maintenance and upgrades after the Migration.
So, this was about the different phases of AWS Migration and how to implement it. Let’s explore the strategies for AWS Migration.
Application Migration Strategies ‘The 6 R’s’
The complexity of migrating existing applications varies, depending on the architecture, Amazon came up with different strategies which they commonly termed as 6 R’s. Let’s look into each of them:
- Rehost:- You have your application ready and working then you can simply Rehost it on AWS. Also referred to “Lift and Shift”. You lift your services and applications from your hosting environment and shift them to cloud using a third party exporting tool.
- Replatform:- You have an outdated version of your application running on your hosting environment so you have to modify your application and then Rehost it. Replatform is a modification of “Lift and Shift”. It involves optimizing the cloud architecture to achieve the benefits without changing the core architecture of the application.
- Repurchase:- There would be certain applications that won’t be compatible with the new architecture. In that case, you need to purchase a new application for the new architecture. AWS Marketplace provides a wide range of services that too with a “Pay as you Use” model. Repurchase is also referred to as “drop and shop” where you upgrade, ease the implementation and accept the new architecture and make changes to the existing model.
- Refactor:- You want to add up new features, scale up the limits of the existing business model and performance that are difficult with the existing environment. You reconsider your needs, though the solution is a bit expensive. Improving business by moving to a service-oriented architecture (SOA) will benefit your business in the longer run.
- Retire:- After AWS Migration you can differentiate between useful and useless resources. Hence, you cut off all the resources that are no longer useful to the business and build a strategy around the new resources. This will cut down the extra cost. With lesser things to worry about, now you can focus on maintaining the resources used by the new business model.
- Retain:- As you know, the sections of your project you need to migrate. You can simply use any of the above-mentioned strategies. Then, build a strategy to retain those applications, which, according to your business model are yet not ready to be migrated to the cloud or the applications that were upgraded recently.
We saw the different strategies, together known as 6 R’s, one should choose wisely while AWS Migration. Now let’s see the bigger picture that lies after implementing AWS Migration.
Benefits Of AWS Migration
AWS Migration gives your organization limitless benefits. Let’s look into the major ones in brief.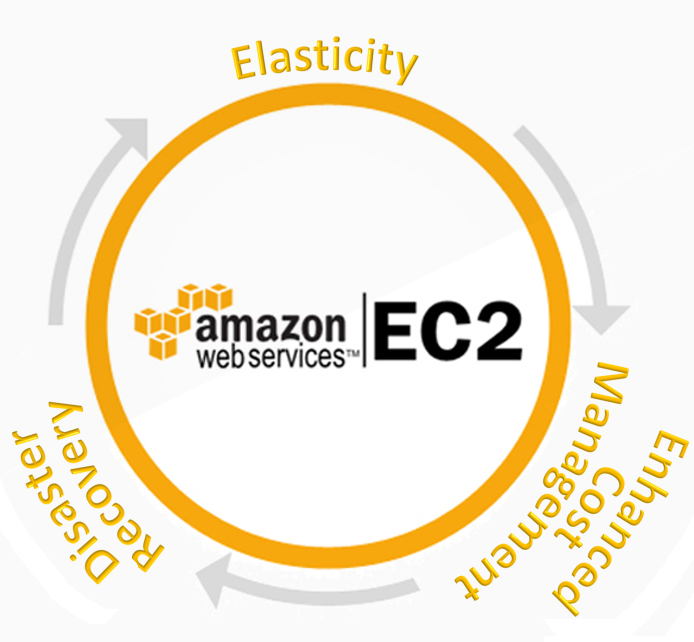
- Elasticity:- Adding and Removing capacity whenever it is needed is the greatest benefits of elasticity.
- Disaster Recovery:- With a 99.95% guaranteed uptime, businesses can be confident knowing that their data will always be available.
- Enhanced Cost Management:- The IaaS platform provides two major benefits. First, an IaaS such as Amazon Web Services is available as a monthly service. Secondly, it eliminates the need to continue to purchase and maintain physical hardware.
These were the benefits of AWS Migration. Let’s jump into the services offered by AWS to ease the process of Migration.
Services For AWS Migration
Out of the many tools provided by Amazon to automate data migration, I’ll be talking about the more commonly used ones.
 AWS Migration hub: AWS provides a single location for tracking Migration process. Migration Hub gives you the freedom to choose the Migration partner and tools that fit your needs.
AWS Migration hub: AWS provides a single location for tracking Migration process. Migration Hub gives you the freedom to choose the Migration partner and tools that fit your needs.
AWS Server Migration service (SMS): AWS SMS is an agentless service that helps migrate loads of  on-premise workload to AWS easier and faster. It allows you to automate Migration and track replication of Server. It makes coordinating with your large scale-server Migration easy.
on-premise workload to AWS easier and faster. It allows you to automate Migration and track replication of Server. It makes coordinating with your large scale-server Migration easy.
![]()
Amazon S3 transfer acceleration: This makes the transfer of files over long range to AWS S3 bucket faster and secure.
AWS Snowball: It is a petabyte-scale data transfer solution that uses secure devices to transfer a  large amount of data in and out of AWS.
large amount of data in and out of AWS.
 AWS Snowmobile: It is an exabyte scale data transfer solution to move an extremely large amount of data to AWS. Snowmobile makes the transfer of massive volumes of data easier.
AWS Snowmobile: It is an exabyte scale data transfer solution to move an extremely large amount of data to AWS. Snowmobile makes the transfer of massive volumes of data easier.
Amazon Kinesis Firehose: It is the easiest out of all the methods. It can capture and automatically load
streaming data into Amazon S3. You can analyze real-time data to get timely insights of Migration.
Now that you know everything about AWS, and AWS Migration, let me show you a use case where you will be migrating a Virtual OS from my local machine to AWS Cloud.
Demo: Implementing Migration using Import/ Export method
You will be migrating an on-premise Virtual OS running on VMWare to AWS using Import/Export (AWS Direct Connect) method.
Pre-requisite
- VMware Workstation installed on your Local Machine
- Running AWS Account
- Created IAM User On AWS
- AWS CLI Configured On Your Local Machine
- Created S3 Bucket on AWS
1. Create a .vmdk export file for Ubuntu 14.04.
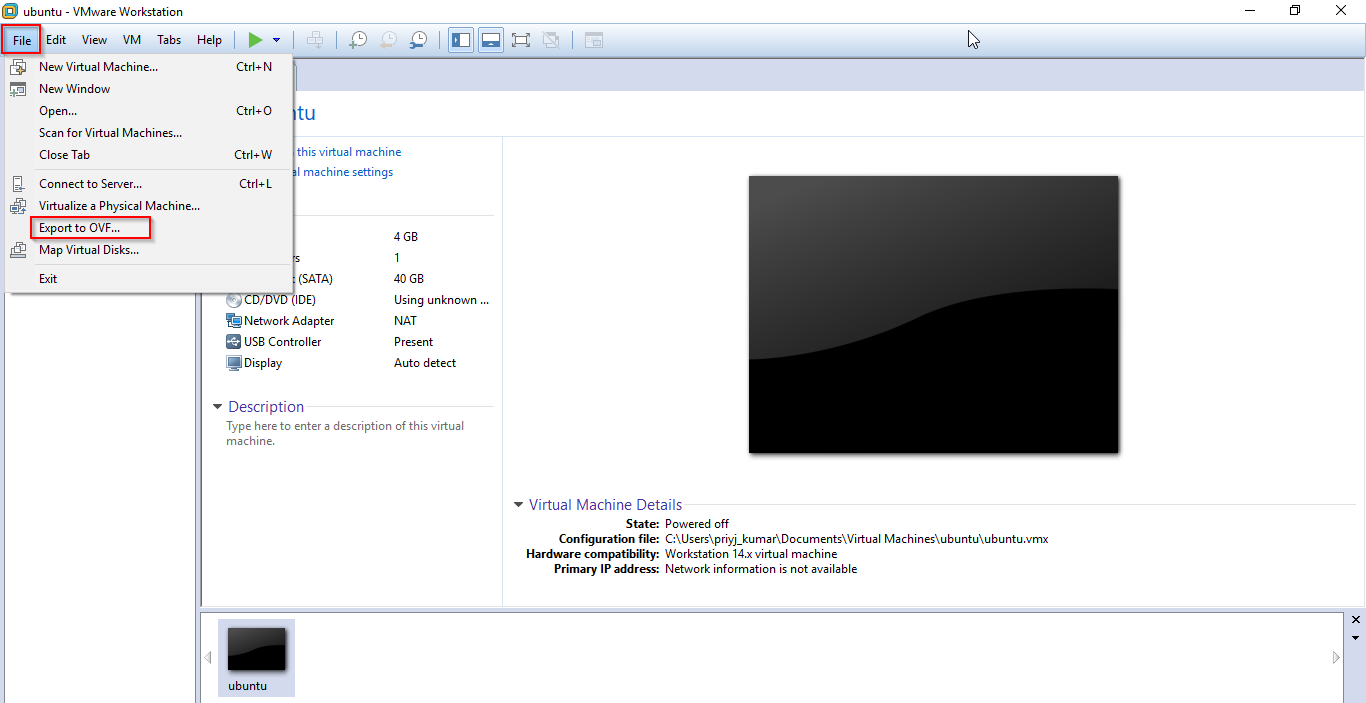
2. Download & configure AWS CLI.

3. Create an IAM User.
Now click on “Add User”.
 Next, select a unique User name.
Next, select a unique User name.
Now give Administrator access.
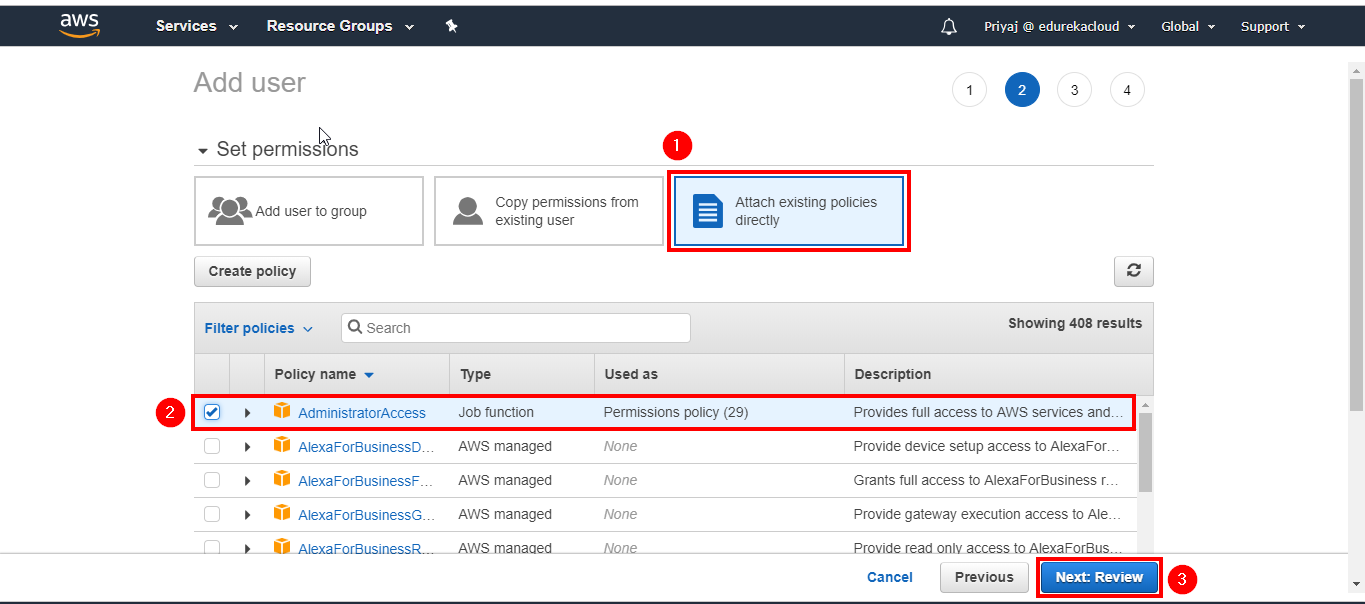
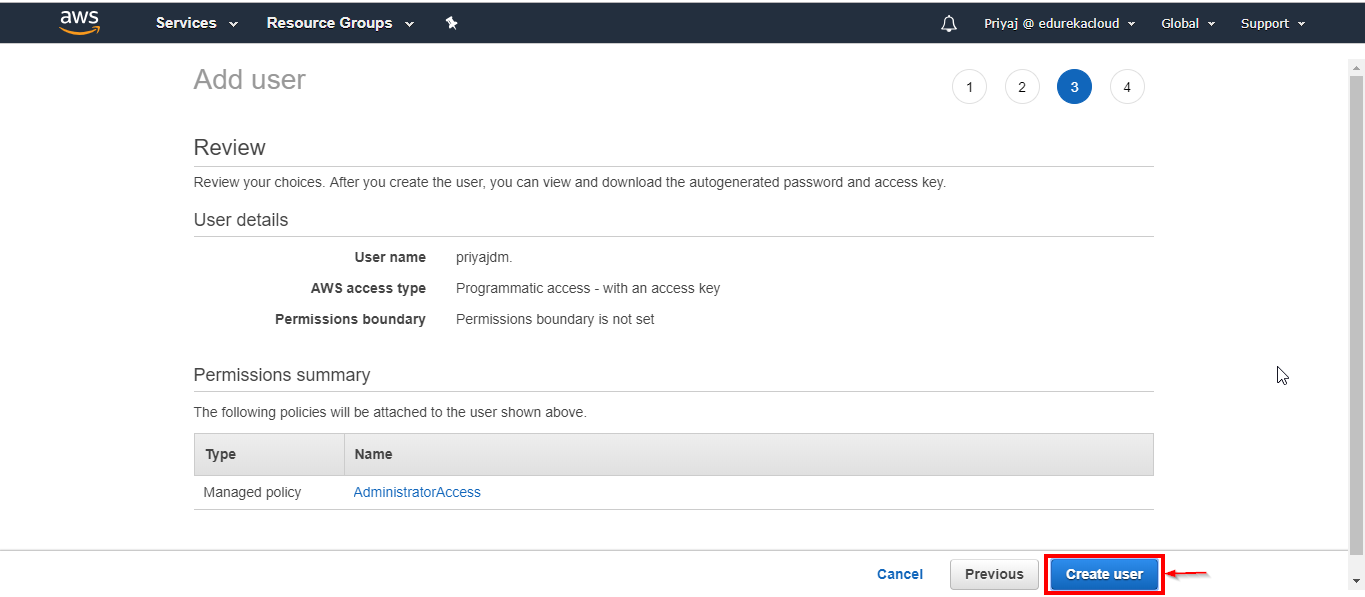
Click on Create User.
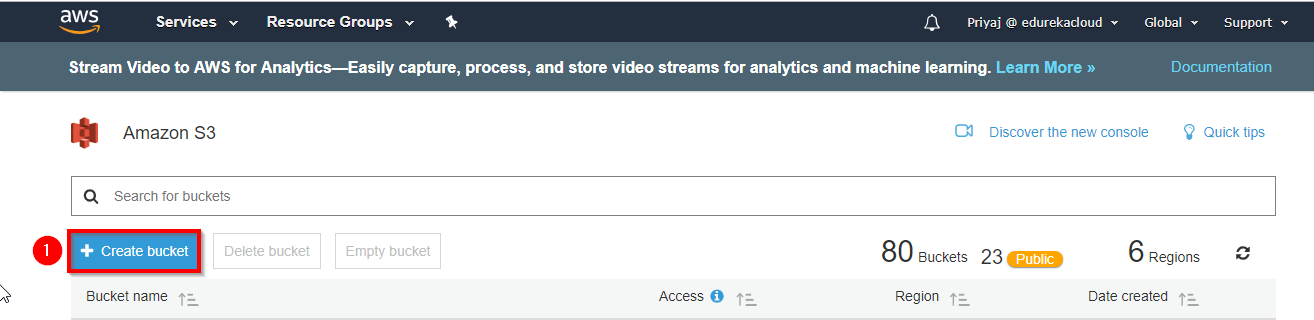
4. Create an S3 bucket and add file(image file of the OS).
Select a unique Username.
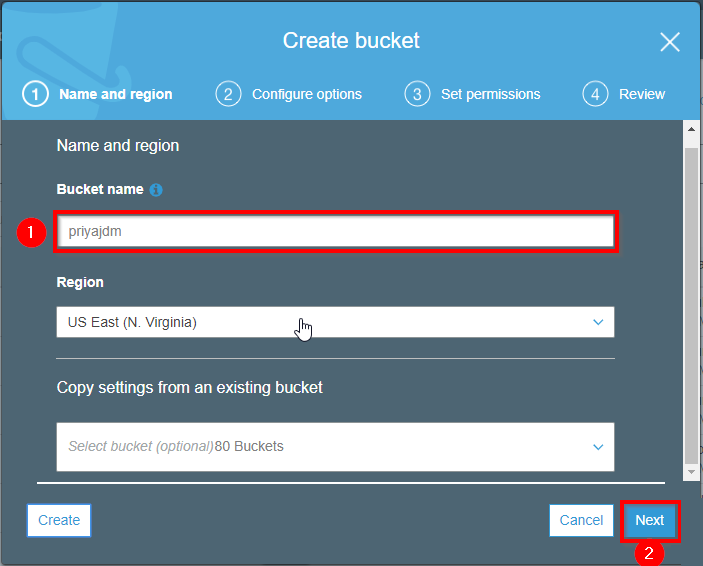
Review and Create Bucket.
Add the exported .vmdk file.
 Click on Upload.
Click on Upload.
Wait till the image reflect on the list.
5. You can upload the file using AWS CLI also.
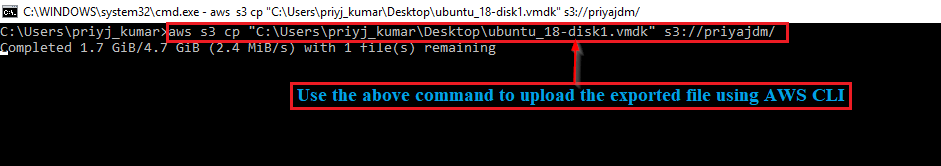
6. Once the file is uploaded, create an AMI for the imported image file.
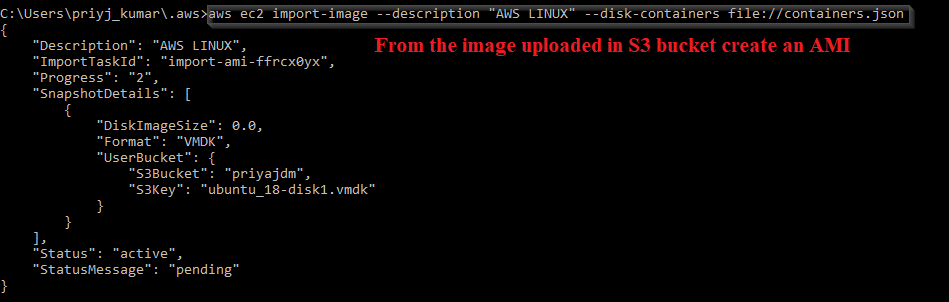
Your image is now available as an AMI.
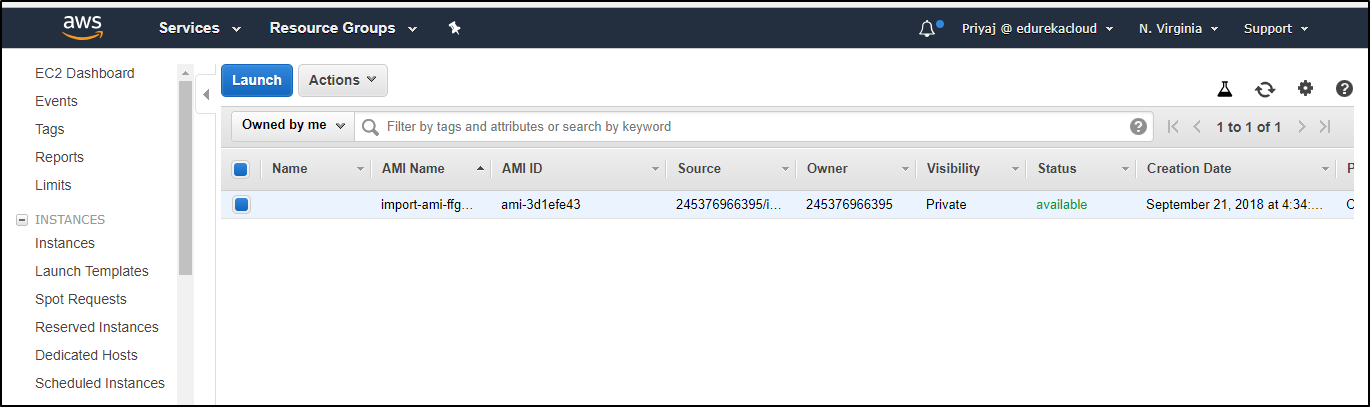
7. You can run the AMI created in two ways:-
7 (a). Using CMDER :
Copy the connection string and paste it to the CMDER Console, it will take few minutes to connect and then will open your Ubuntu 14.04.
7 (b). Using Putty :
Configure the .pem file to your Putty and provide the username and the connection string. It will show initializing and few minutes later you will land on to Ubuntu 14.04.
In this way, we have successfully migrated a virtual OS on AWS. I hope you enjoyed reading this AWS Migration article.
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
- The 6 R’s
- Rehost (“lift and shift”)
- Move applications to AWS without changes. In large-scale, legacy migrations, organizations are looking to move quickly to meet business objectives.
- Applications may become easier to re-architect once they are already running in the cloud. This happens because the hard part, which is migrating the application, data, and traffic, has already been accomplished.
- Replatform (“lift, tinker and shift”)
- You are making a few cloud optimizations in order to achieve some tangible benefit without changing the core architecture of the application.
- Replatforming Tools
- Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for relational databases – AWS manages the database application for you, so you can focus on the application of the database itself
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk – a fully managed platform where you can simply deploy your code, and AWS will handle scaling, load balancing, monitoring, database and compute provisioning for you
- Repurchase (“drop and shop”)
- Move from perpetual licenses to a software-as-a-service model. For workloads that can easily be upgraded to newer versions, this strategy might allow a feature set upgrade and smoother implementation.
- For example, you will discontinue using your local VPN solution and instead purchase a commercial VPN software from AWS Marketplace such as OpenVPN for AWS.
- Refactor / Re-architect
- Re-imagine how the application is architected and developed using cloud-native features.
- Typically, this is driven by a strong business need to add features, scale, or performance that would otherwise be difficult to achieve in the application’s existing environment.
- This migration strategy is often the most expensive solution.
- Retire
- Identify IT assets that are no longer useful and can be turned off. This will help boost your business case and direct your attention towards maintaining the resources that are widely used.
- Retain
- Retain portions of your IT portfolio if there are some applications that are not ready to be migrated and will produce more benefits when kept on-premises, or you are not ready to prioritize an application that was recently upgraded and then make changes to it again.
- Rehost (“lift and shift”)

- The following strategies are arranged in increasing order of complexity — this means that the time and cost required to enact the migration will be proportional to the increase, but will provide greater opportunity for optimization
- Retire(simples) < Retain < Rehost < Repurchase < Replatform < Re-architect/Refactor (most complex)
- Consider a phased approach to migrating applications, prioritizing business functionality in the first phase, rather than attempting to do it all in one step.
- General Migration Tools
- AWS Migration Hub – provides a single location to track the progress of application migrations across multiple AWS and partner solutions. Using Migration Hub allows you to choose the AWS and partner migration tools that best fit your needs, while providing visibility into the status of migrations across your portfolio of applications.
- AWS Application Discovery Service – collects and presents configuration, usage, and behavior data from your servers to help you plan your migration.
- AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) – an agentless service for migrating thousands of on-premises workloads to AWS.
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) – helps you migrate databases to AWS. The source database remains fully operational during the migration.
- AWS Snowball – a petabyte-scale data transport solution that uses secure appliances to transfer large amounts of data into and out of AWS.
- AWS Snowmobile – an exabyte-scale data transfer service used to move extremely large amounts of data to AWS.
- AWS Direct Connect – lets you establish a dedicated network connection line between your network and one of the AWS Direct Connect locations.
- Amazon Kinesis Firehose – a fully managed service for loading streaming data into AWS.
- AWS Marketplace – where you can purchase different types of software and licenses offered by AWS Partners and other AWS Users.
Are you thinking about AWS Migration, and moving on-premise projects to the cloud?
But don’t know where to start and how to go about it?
In this post, I am going to guide you through the AWS and AWS Migration.
What is AWS?
AWS or Amazon Web Services is one of the most popular cloud platforms, with over 175 web services with data centers across the globe. Millions of customers, ranging from fastest growing enterprises, large corporations, and government agencies, to medium business owners, are using the AWS.
AWS is a cloud service provided by Amazon, and it is easy to use, scalable, and customizable, and innovative.
More and more businesses are moving to the cloud, and the AWS is a leading cloud platform.
What is AWS Migration?
AWS Migration is the process of moving data, applications, or other business components from an organization’s on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, or moving them from one cloud service to another.
2.5x quintillion new bytes of data generated each day.
With so much data around, cloud migration is an ideal solution today.
Business is no easy task when it comes to handling situations like security, scaling up or down, etc. Let’s look at a few scenarios where AWS Migration could be a better resort.
Need for Migration
According to recent stats, it is estimated that by 2020, more than 1/3rd of the data will pass through the cloud. Well, it would be better to learn swimming than to sink.
There are many reason to move migrate to the cloud.
- The website/application has started getting a high volume of traffic
- For fast application implementation and deployment
- Modernize current IT asset base
- Prepare for future needs
- Lower infrastructure costs
- Increase Business Agility
- Disaster Recovery
- Security
How to Migrate On-Premise Server to AWS Cloud?
Migrating your existing applications to the AWS Cloud involves 3 steps:
- Before AWS Migration
- During AWS Migration
- After AWS Migration
Before AWS Migration Stage
1. The goal of migration to Cloud
Goal 1: My business is growing, and my site usually goes down because of high-traffic, what should I go for?
Ans: Public or Private cloud
Goal 2: I have made enough investments for on-premises storage; how can I get the best of Cloud alongside?
Ans: Hybrid
2. Staff Training
It is essential to train the staff early in the process. This will help you with:
- Smoother transition
- Easier to dissipate FUD and break down barriers since you have more knowledgeable internal teams.
Make sure this step takes place before you make organization-wide decisions on the improvising your IT asset.
You May Also Like: Migrating from t1.micro to t2.micro in AWS
3. Selecting Right Partners
Well, if you have the right partners for managed aws by your side, the journey will be smoother and more effective. But how to find your AWS soulmate?
- Look for the ones having the technical expertise and good experience in migrating to AWS.
- Experts are having the right project management framework and agile methodology.
- Check on if your cloud partner can help facilitate the operational model you plan on adopting. Since the AWS certified partners have the right expertise to assist in hassle-free migration.
During Migrating to AWS
Before further moving to how of the cloud migration process, here’s a formula suggested by AWS to determine how much data can be transferred and how fast.
Number of Days = (Total Bytes)/(Megabits per second * 125 * 1000 * Network Utilization * 60 seconds * 60 minutes * 24 hours)
AWS Migration: 5 Cloud Migration Steps
Following are the 5 AWS Migration steps:
- Planning and Assessment
- Migration Tools
- AWS Cloud Storage Options
- Migration Strategies
- Application Migration Options
1. Planning and Assessment
The planning and assessment phase is divided into:
- Financial Assessment
- Security & Compliance Assessment
- Technical and Functional assessment
1.1 Financial Assessment
Before deciding on-prem to cloud migration, you need to estimate the cost of moving data to the AWS cloud. A careful and detailed analysis is required to weigh the financial considerations of on-premises center versus employing a cloud-based infrastructure.
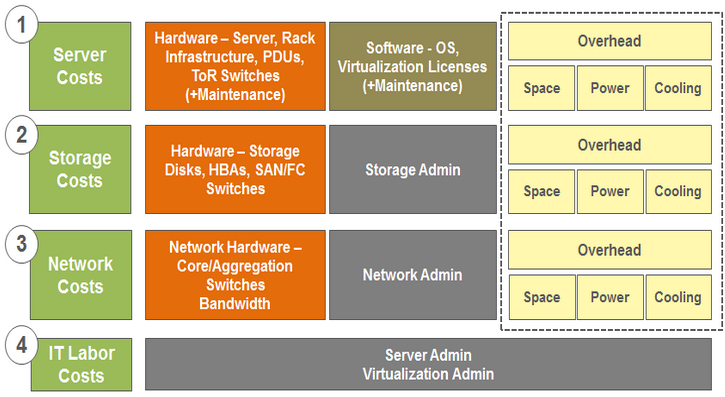
P.S. You also need to evaluate the on-premises costs which include server cost, storage cost, network cost, and IT labor costs.
1.2 Security and Compliance Assessment
If you are wondering about:
- Overall risk tolerance
- Main concerns around availability, durability, and confidentiality of your data.
- Security threats
- Options available to retrieve all data back from the cloud
Then it is better to involve your security advisers and auditors early in this process. Since data security is a challenging task, therefore, you must understand your threats, risks, and based on that classify the data into different categories. This will help you know which datasets to move to the cloud and which ones to keep in-house.
You Can’t-Miss: DigitalOcean vs. AWS EC2
1.3 Technical and Functional Assessment
Assessing the need to understand which applications are more suited to the cloud strategically and architecturally. This helps you decide:
- Which application/data to move into the cloud first?
- Which data to transfer later?
- Which applications should remain in-house?
Questions you should ask yourself before moving data into the cloud:
- Which apps should the business move to the cloud first?
- Can we reuse our existing resource management and configuration tools?
- How can we get rid of support contracts for hardware, software, and network?
- Does the cloud provide all of the infrastructure building blocks we require?
2. AWS Migration Tools
There are physical limitations when it comes to migrating data from on-premises locations into the cloud. That’s where migration tools come to rescue. The following tools will help you move data through roads, networks, and technology partners.
Detailed Guide: AWS migration tools and Services
2.1 Unmanaged Cloud Data Migration Tools
If you need easy, one-and-done methods to transfer data at small scales, go for the following tools:
- Glacier command line interface- On-premises data → Glacier vaults
- S3 command line interface- Write commands → Data moves directly into S3 buckets
- Rsync- Open source tool combined with 3rd party file system tools. Copy data directly → S3 buckets
2.2 Amazon Managed Cloud Data Migration tools
Based on optimizing or replacing the internet and friendly interfaces to S3, there are the following tools you can leverage:

A. Optimizing or Replacing the Internet
Ideal for moving data lakes, extensive archives and more.
| Ideal for | Data Migration Tool to Be Used | |
| 1. | Migrate petabytes of data in batches to the cloud | AWS Import/Export Snowball |
| 2. | Migrate exabytes of data in batches to the cloud | AWS Snowmobile |
| 3. | Connect directly into an AWS regional data center | AWS Direct Connect |
| 4. | Migrate recurring jobs (with incremental changes over long distances) | Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration |
B. Friendly Interfaces to S3
Makes it simple to use S3 with existing native applications. Helps you to integrate existing process flows like recovery, backup, etc.
| Ideal for | Data Migration Tool to Be Used | |
| 1. | Push backups or archives to the cloud with least disruption | Technology Partnerships |
| 2. | Cache data locally in a hybrid model | Gateways (AWS or Partner) |
| 3. | Collect and ingest multiple streaming data sources | Amazon Kinesis Firehose |
| 4. | Migrate petabytes of data in batches + apply onboard storage + compute capabilities | AWS Snowball Edge |
3. Various Storage Options Available in the AWS Cloud
Decide which storage option is feasible for you based on:
- Cost,
- Durability,
- Latency performance (response time),
- Availability,
- Size of the object stored (large, small),
- Accessibility,
- Cache-ability,
- Consistency (eventual, strict),
- Relational (SQL joins)
- Update Frequency
Which Storage Option to Use?
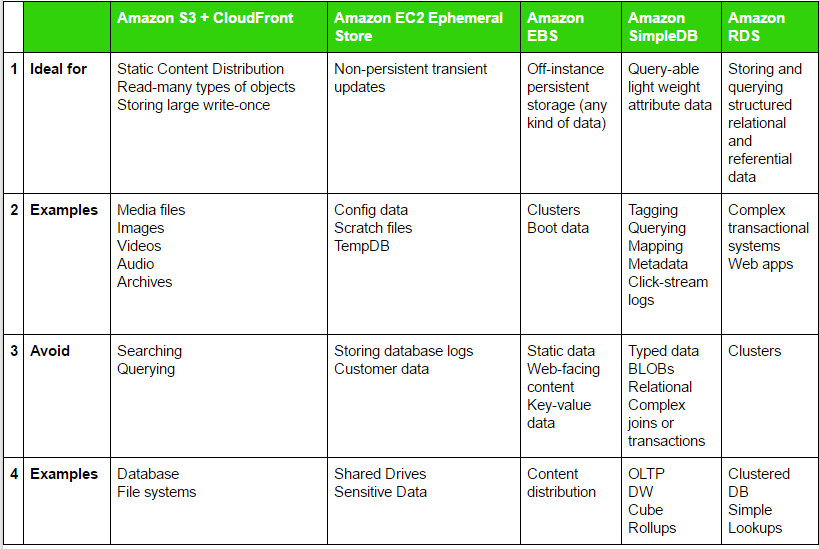
4. 2 Major Strategies for AWS Migration
Here are two strategies that will help you move part of or an entire system to the cloud without disrupting the current business:
1. Forklift Migration Strategy
Self-contained applications, tightly coupled applications, or stateless applications might be better served by this approach. “Pick it all up at once and move it to the cloud” approach.
Pros
- Shrinking IT infrastructure footprint: Using this approach for specific application types, you have to worry less about the IT infrastructure.
- Focus on Other Important Resources: With this approach, you will be able to focus on your core and differentiating resources to be ahead of the competition.
Cons
- Might not be able to take immediate advantage of scalability and elasticity of the cloud
2. Hybrid Migration Strategy
Considering some parts of an application and moving them to the cloud while leaving other parts of the application in place. Ideal for large systems involving several applications.
Pros
- Low-risk approach to the migration of applications to the cloud.
- Parts can be moved and optimized one at a time.
- Reduced risk of unexpected behavior after migration.
Cons
- Time-consuming.
Configuring and Creating AMI
- AMI provides the information needed to launch an instance. This is provided by AWS or solution provider.
- You will need to create an AMI for each component designed to run in a separate Amazon EC2 instance.
- Create an automated or semi-automated deployment process to reduce efforts and time.
- Think of a process for configuration management to ensure your servers running in the cloud are included in your process.
5. Application Migration Options

Well… here are some appropriate application migration options available:
1. Live Migration
The process of moving a running application from physical machines to cloud without disconnecting the application. Memory, network connectivity, and storage of the virtual machine are replicated from the physical device to cloud.
2. Host Cloning
It is cloning the Operating System image and typically one-time migration.
3. Data Migration
Synchronizing the data between computer storage types or file formats to the cloud. The data is selectively pushed to AWS Cloud.
4. App Containerization
An OS-level virtualization method for deploying and running distributed applications.
5. VM Conversion
Converts Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) into AWS recognizable format. The data is transferred via API.

The level of Efforts Required with Each Migration Method:

Post AWS Migration Stage
1. Leveraging the Cloud
After migrating your application, don’t forget to run the necessary tests, and confirm everything is in place. Invest time and resources to explore the additional benefits of the AWS cloud. You must:
- Leverage AWS Enterprise Support
- Leverage other AWS services like Auto Scaling Service, Amazon CloudFront, and Amazon Elastic MapReduce.
2. Monitor and Optimize
Understand → Monitor → Examine → Observe
Follow this to know your load patterns and manage the cloud environment more effectively. Since AWS charges only for the infrastructure (having utility pricing structure) that has been used, you can cut cost here by optimizing your systems.
You May Also Like: Plesk vs. cPanel
3. Use Cloud Monitoring Tools
There are various tools available that help in application-level insights and monitoring on AWS. Some of them are:
- New Relic
- AWS CloudWatch Logs
- APPDYNAMICS
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Cloud Secure?
49% of IT decision-makers admitted they are ‘very or extremely anxious’ about the security implications of cloud services. There is a lot of myths surrounding to cloud security. Undoubtedly, without the right amount of planning and advanced technology, cloud-based platforms are as risky as your existing enterprise systems.
Must Read: Why Google is Forcing You To Have SSL Certificates
How does the cloud work with my existing on-premise investments?
If you already have made on-premise investments, you can still work in a hybrid cloud model.
Challenges Faced In AWS Migration
Some of the challenges faced by the companies while AWS migration is:
- Lack of details and scope concerning security, operating system, compliance, etc
- Limited or no accurate tools for discovery and process
- Lack of application contexts/ info
- Similar data storages/limited CMDB
- Inaccurate on-premises cost
These challenges lead to increased costs, longer time to value, and inaction. Therefore, it becomes crucial to do a detailed analysis of the business needs and available options.

Factors Influencing a Successful Migration
- The complexity of Application Architecture
- How loosely coupled your application is?
- Efforts Required: how much effort you are willing to put into migration
Conclusion
In this post, I mentioned all the vital things related to the AWS migration.
I hope this article helps you.
In this course we will learn to recognize and explain the migration services available from AWS and AWS partners, and how to run a migration using the AWS Server Migration Service. This course is a blend of instructional learning and demonstration. In this course we cover the following topics:
- The AWS Migration Hub - which provides a simple way to manage migration of severs and applications.
- The AWS Discovery Services -we explore the AWS Discovery Connector and the Discovery Agent which enable us to audit and quantify a migration project.
- The AWS Server Migration Service - which provides a way to manage migrating vmware and HyperV virtual machines to the AWS Cloud.

Comments
Post a Comment